Otoplasty literally means “ear changing,” and for someone embarrassed by prominent ears, it can also be life changing. Prominent ears can draw undesired attention. Protruding ears can cause problems for young children vulnerable to taunting by peers and adults who may feel uncomfortable wearing their hair back or getting short haircuts. Our experienced plastic surgeon, Dr. Joseph Mele, can create a customized otoplasty treatment plan designed to successfully reduce the appearance of prominent ears in both adults and children.
What is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty is a cosmetic surgery procedure used to correct prominent or large ears. Also referred to as ear pinning, otoplasty brings protruding ears back against the side of the head. The exact method of otoplasty treatment depends on the source of the problem.
Every otoplasty needs to be individualized; however, there are three main areas that need to be considered in every case. Three anatomic variations can lead to prominent ears, and each has its own set of maneuvers used to correct them. While any of these variations can cause the ears to protrude, it is not unusual for two or even all three factors to be present. Additionally, asymmetry is the rule rather than the exception. It is common for one ear to be affected more than its partner, and each ear needs to be evaluated separately.
Otoplasty Before-and-After Pictures
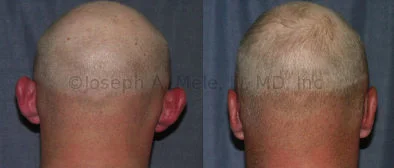

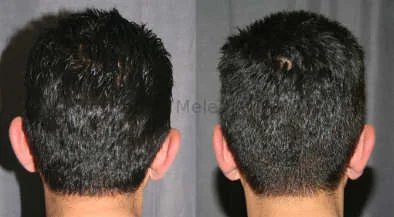
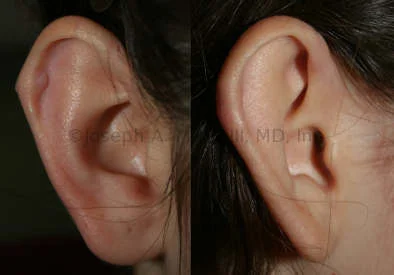
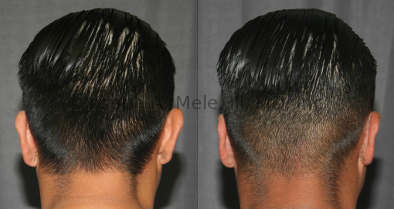

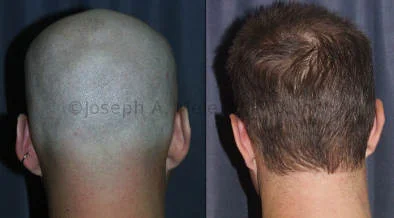
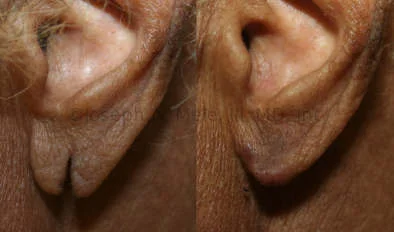
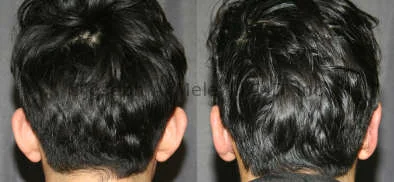
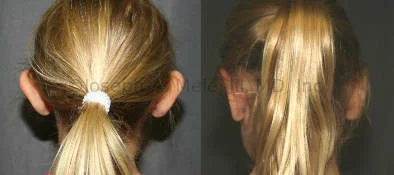


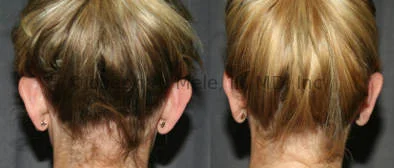
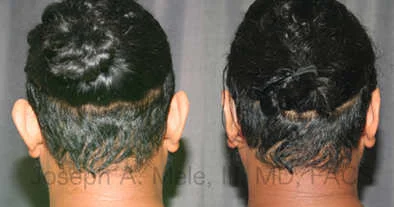

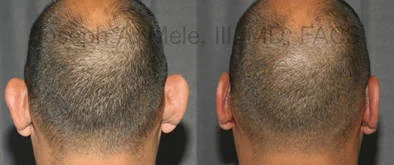
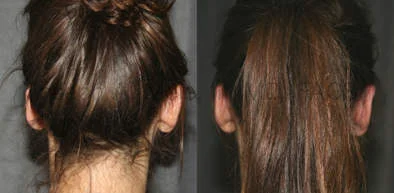

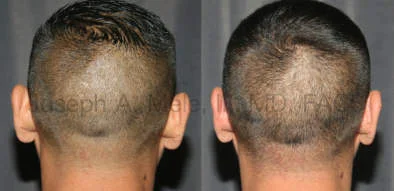
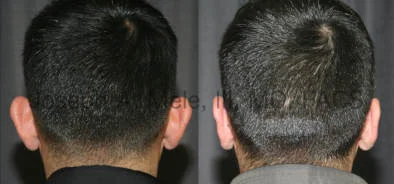
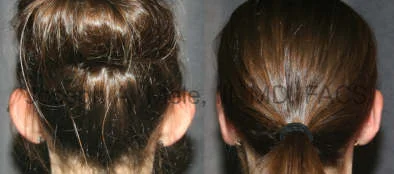
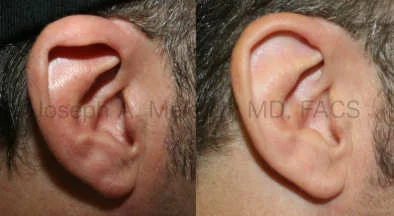
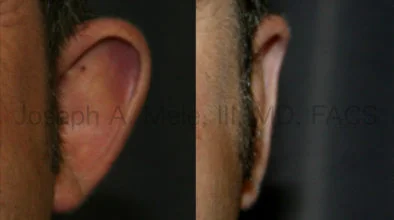
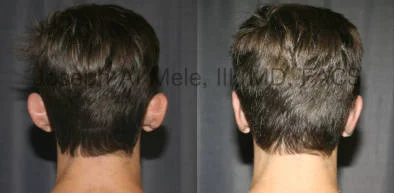
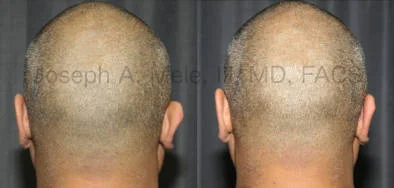
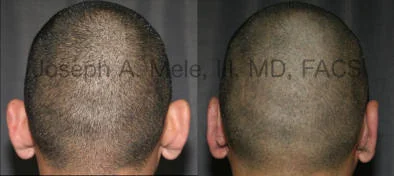
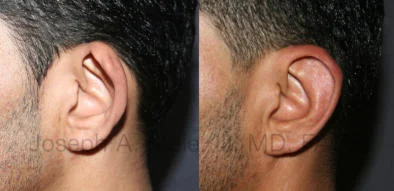
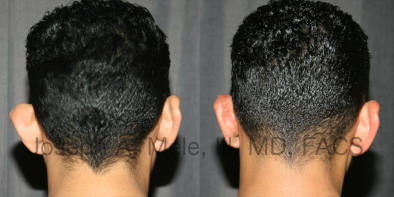

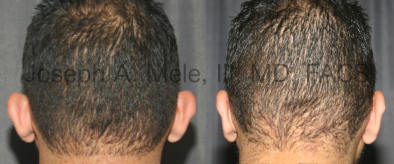
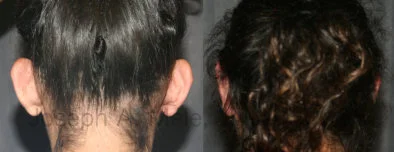

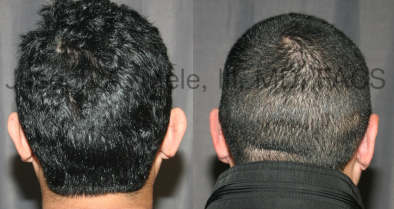
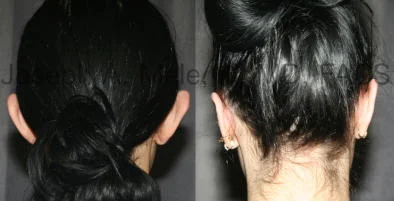
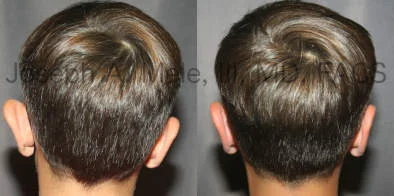
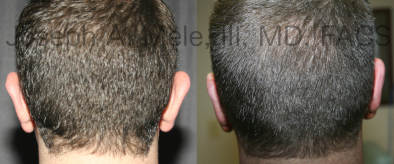
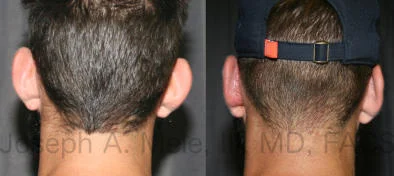
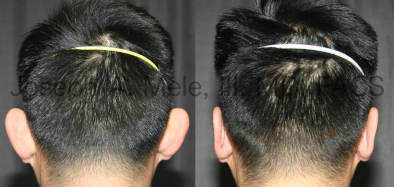
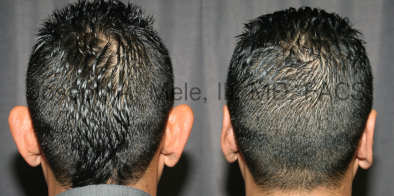
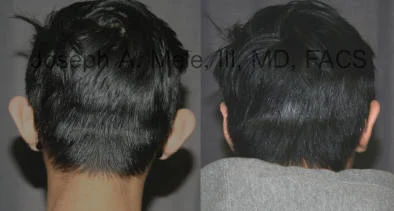



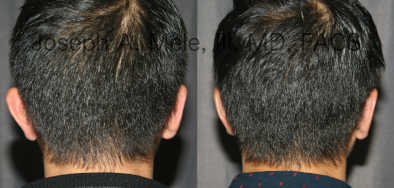

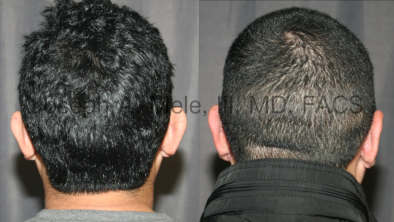

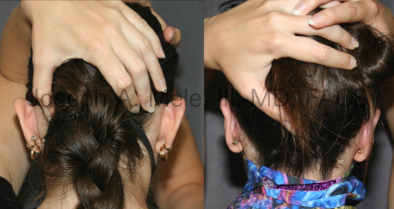
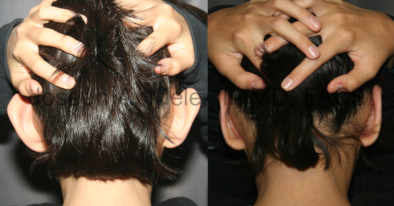
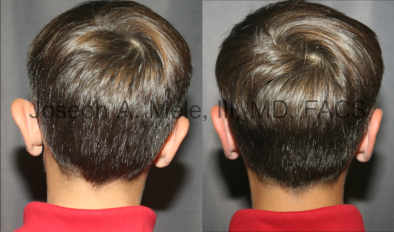
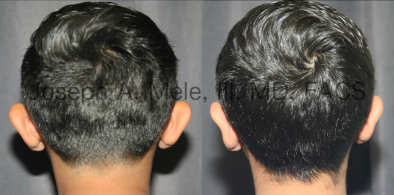
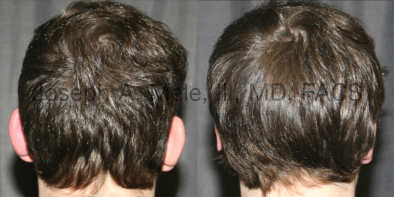
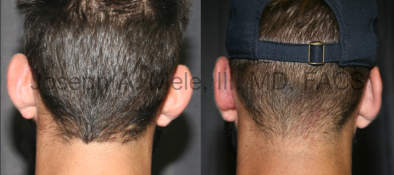
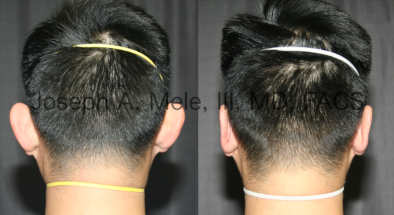
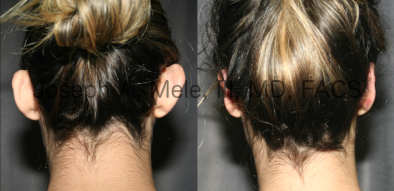
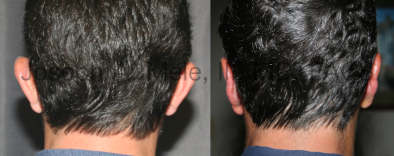

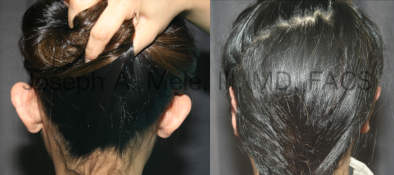
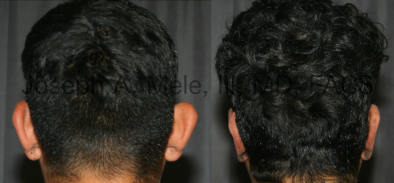
The cosmetic ear surgery before-and-after picture gallery above has examples of otoplasty for prominent ears. Additionally, examples of repairs for torn earlobes and for cartilage deformities from helical ear piercings are also shown. As you can see from the otoplasty before-and-after photos, cosmetic ear surgery is performed for adult men and women as well as children.
Otoplasty Videos
Who Is a Candidate for Otoplasty?
If you feel your ears are too obvious, or that they stick out too much, then read on. Otoplasty is designed to help precisely these situations. With a combination of folding and setting back the cartilage of the ear, ears that protrude are brought back into proper perspective.
The minimum age for otoplasty is five. By the age of five the ears are almost fully grown, and surgery can be safely and predictably performed. As long as you are healthy, there is no maximum age. Otoplasty is sometimes combined with facelifts for patients who have prominent ears and also desire facial rejuvenation.
As with any elective surgery, safety is of the utmost importance. Since this procedure is usually performed on younger patients, other medical problems are not common. If you have a medical condition, however, be certain to let Dr. Mele know. As long as the condition is controlled, otoplasty can be safely performed in most situations.
Some medications can interfere with healing or cause increased bleeding. Your preoperative evaluation will include how to manage any medications, vitamins, supplements, or herbal medications around the time of surgery. Be certain to bring a list of these to your consultation appointment.
While the most common reason for otoplasty is to correct ears that stick out, otoplasty also includes the repair of many other ear deformities. Birth defects such as Stahl’s ear, cupped ear, “Spock” ears, or incomplete ear development can be improved. Acquired defects, such as torn earlobes, over-gauging, keloids, or other ear injuries are other areas that can be addressed. More on earlobe repair is included below.
What Causes a Prominent Ear?
The ear is a very complex piece of anatomy. The external ear alone arises from six different swellings on the side of the embryo’s head. Failure of these swellings to form or fuse together leads to a wide variety of ear deformities. Even when the pinna (the soft external ear) forms normally, a series of folds are required to give the ear its final shape.
Prominent Ears – Folding Problems
Failure of the edge of the ear to fold backwards is the most common cause of prominent ears. Folding problems may involve the entire pinna, but can also be isolated to the top of the ear. Without this fold, the central cup of the ear extends out to the edge, projecting the ear’s edge further away from the head. Formation of the fold is key to the formation of a less prominent, cosmetically pleasing ear.
Prominent Ears – Size Problems
Sometimes the ear is prominent because of its enlarged size. Most commonly, it is the central cup of the ear that overdevelops. The result is a prominent central cup that either overpowers a normally folding ear, or the large central ear cup adds to the problems caused by a lack of a fold in the rim. The two problems compound each other to increase the overall prominence. With large ears, just forming a normal fold may not be enough, and some cartilage may need to be removed.
Prominent Ears – Rotation Problems
The least common cause of prominent ears is when the ear develops normally, but is rotated forward and away from the head. This anatomic variation can further compound the folding and size problems listed above, but requires additional treatment for optimal results. Like most plastic surgery, the results depend on making the correct diagnosis and carefully correcting each problem.
Other Types of Otoplasty
Prominent ears are by far the most common reason for otoplasty; however, otoplasty is also performed for other ear deformities, such as:
- Cauliflower Ear – Also known as boxer’s ear or wrestler’s ear, cauliflower ear is an acquired deformity caused by trauma to the ear and is often seen in MMA fighters, boxers, and wrestlers. Trauma to the ear causes bleeding under the skin, also known as a hematoma. If not drained, this collection of blood becomes organized, hard, and often calcified. Treatment consists of making an incision and removing the old hematoma. It is better to seek early treatment because once a cauliflower ear has formed, complete correction is unlikely.
- Stahl’s Ear (“Spock Ears”) – Sometimes a third fold (crus) forms in the upper ear that points backwards, giving the appearance of an elf’s ear (or “Spock” ear for Star Trek fans). Treatment involves reshaping the cartilage. The two main methods are remodelling the cartilage to flatten the fold for mild deformities or removing the affected area of cartilage and flipping it over when more severe.
- Cupped Ears (Constricted Ears, Lop Ears) – When the top of the ear is folded forward onto itself, it is termed a cupped ear. In this case, the skin and the cartilage may be insufficient to easily straighten out. In most cases, the skin and cartilage can be rearranged; however, in some cases skin and cartilage grafts are required.
- Anotia/Microtia (Goldenhar syndrome) – Sometimes the outer ear does not form. In these cases, hearing may also be affected, sometimes severely. This condition may be associated with other congenital deformities. Anotia and microtia are easily recognized at birth and often are treated at a Children’s Hospital by a team of specialists including a plastic surgeon. Anotia is the most severe case as no external ear or opening is present. Microtia may involve the absence of part or most of the external ear. Both conditions should be evaluated by an experienced craniofacial team.
- Cryptotia (Hidden Ear) – The cartilage of the upper ear is often present; however, it is buried beneath the scalp skin. Treatment involves exposing the cartilage and covering it with skin.
Earlobe Repair and Other Ear Surgery Options
Ear changing (but not necessarily otoplasty), earlobe repair, earlobe reduction, gauge closure, and other post-traumatic injuries are also amenable to surgical repair. Often, these are performed in the office under local anesthesia.
The Timing of Otoplasty
Otoplasty is one of the few cosmetic plastic surgery procedures that is often performed on children. By five years of age, the ear is already 85% the size of an adult ear, so otoplasty can be performed safely and with predictably good results at 5 years of age and older.
How is Otoplasty Performed?
Otoplasty is an outpatient surgical procedure that can be performed under local anesthesia, with or without sedation. For children, general anesthesia is frequently employed to avoid complications associated with movement during surgery. Anxious adults can also benefit from general anesthesia. For adults, the option of performing otoplasty with only a local anesthetic or a local anesthetic with mild sedation can speed recovery and avoid the tiredness and occasional nausea that some experience with general anesthesia.
The procedure is performed through an incision placed in the fold behind the ear. This keeps the scar out of sight, and allows for the removal of some skin from behind the ear to help keep the ear closer to the head. Sometimes a small incision is used in the fold of the ear to further shape the ear cartilage.
What Can I Expect During Otoplasty Recovery?
After otoplasty, the head is wrapped to protect your results and to enhance comfort. Patients are encouraged to sleep on their backs with their heads slightly elevated for the first week. Ear discomfort ranges from patient to patient. The ears are most sore the first day or two after surgery and tapers down from there. Medication is prescribed, but it is not always needed.
It is important to protect the otoplasty repair, especially while sleeping. After the operative head dressing is removed, a sweat band is worn during sleep for three months to prevent recurrence.
Normal activities with the head elevated can resume quickly with the head dressing intact. You should avoid bending over, straining or elevating your blood pressure for the first week. No contact sports, or other activities which are likely to cause trauma to the ears, are allowed for six weeks.
Are Otoplasty Scars Noticeable?
Swelling and bruising are common after otoplasty; however, the magnitude is variable. For some, the ears look normal at the one-week unveiling except for minor swelling. If bruising occurs, it is usually resolved in one or two weeks.
The otoplasty incisions are made behind the ears, so they are hidden from view, especially if you have long hair. Scars are usually difficult to see once fully healed. Thick scars and keloids can occur, and occasionally require revision, but this is rare.
Moisturizer and silicone-based scar creams are used once the head dressing is removed to help speed healing.
How Much Does Otoplasty Cost?
Otoplasty is an outpatient surgical procedure. It can be performed under local or full anesthesia. The cost varies with the type of anesthesia selected and the length of time needed for your procedure. Estimates are available immediately after consultation, and a price range can be obtained by calling the office at (925) 943-6353.
For your convenience, all major credit cards are accepted and financing options are available via third parties. More information about financing is available on our Plastic Surgery Financing page.
Otoplasty Consultations
To learn more about otoplasty, either for yourself or your child, please call our Walnut Creek Plastic Surgery center at (925) 943-6353, or submit your request via the contact form on this page.